What is apheresis?
Apheresis is a wide range of medical technologies that treat diseases by separating and removing various blood-related factors in the body through extracorporeal circulation. It is intended to improve pathological conditions by separating and removing liquid factors such as pathogenic antibodies, inflammatory cytokines, metabolites, and toxic substances, as well as cellular components such as lymphocytes, granulocytes, and viruses, through membrane filtration and adsorption (1).
Currently, apheresis is indicated in a variety of areas, including gastrointestinal, skin, renal, neurological, organ transplantation, and infectious diseases, and the number of indications is expected to increase in the future.
Benefits of using Xenoligo technology for apheresis
There are two methods for adsorption and removal of blood components in apheresis: plasma adsorption (PA; Plasma adsorption) and hemoadsorption (HA; Hemoadsorption).
Dextran sulfate, amino acids, and activated carbon are used as adsorbents. While these adsorbents can remove multiple disease-causing components due to their binding mode and can be used for a wide range of diseases, they have the potential to cause nonspecific adsorption.
Therefore, we are developing next-generation apheresis adsorbents with high adsorption separation efficiency and therapeutic efficacy by taking advantage of the features of Xenoligo®, such as target specificity and stability in blood due to mini hairpins. We also believe that the rapid renal clearance and low placental permeability, which are characteristics of aptamers in general, will enable us to provide apheresis therapies with fewer side effects.
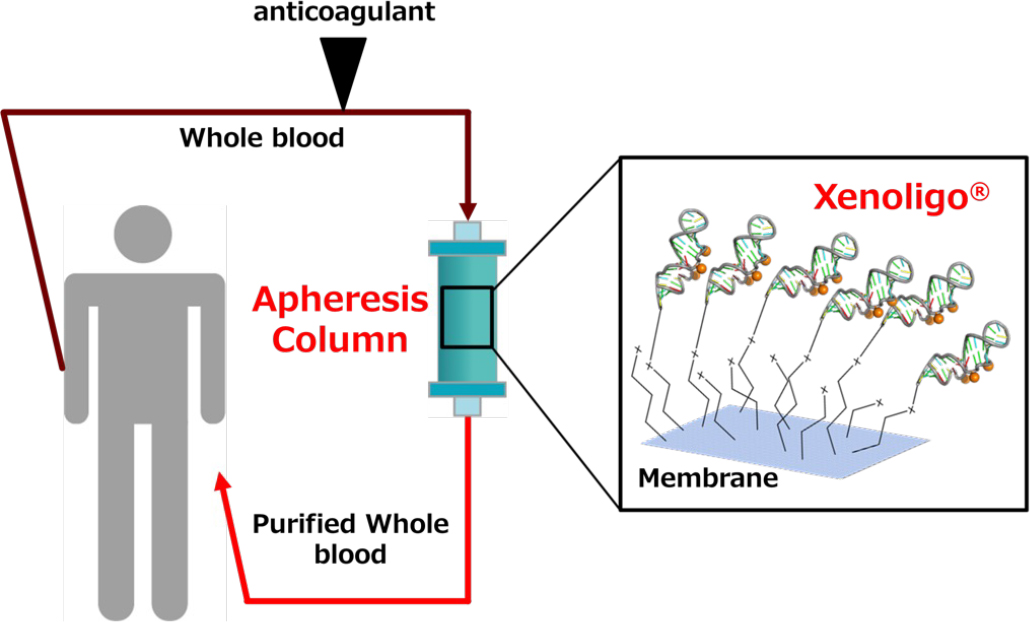
Figure 1: Concept of next-generation apheresis (HA) using Xenoligo®.
[Reference]
- 一般社団法人 日本アフェレシス学会 Web site:https://www.apheresis-jp.org/
IFNg Removal by TAGX-0003 Conjugate Polymer
To obtain POC for apheresis application of Xenoligo®, TAGX-0003 conjugate polymer was prepared by reacting NHS-based polymer with TAGX-0003 with amino modifier. Removal experiments of human IFNg using this conjugate polymer showed that TAGX-0003 maintains its binding activity even when immobilized on the polymer (Fig. 1). In addition, the results of experiments using the autoclaved conjugate polymer showed that the activity of TAGX-0003 was equivalent to that of the untreated conjugate in preparation for the development of actual apheresis devices.
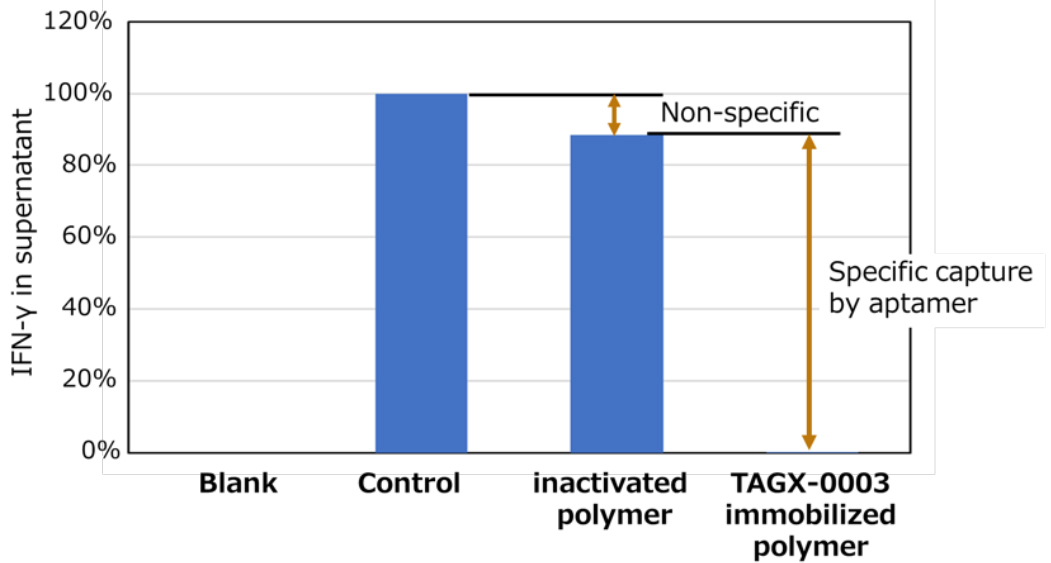
Figure 1. Human IFNg Removal by TAGX-0003 Conjugate Polymer
Cytapheresis
Next-generation apheresis with Xenoligo ® is not limited to the removal of liquid factors, but can also be applied to cell separation (Cytapheresis).
When we performed cell separation experiments by immobilizing Xenoligo® on magnetic beads with a specific membrane protein that we have already obtained (Figures 1 and 2), we found that cells could be removed in a density-dependent manner with Xenoligo® on the beads. This indicates that Xenoligo® can be applied to the treatment of diseases caused by specific cell types present in the blood.
Magnetic separation of specific cell by Xenoligo®
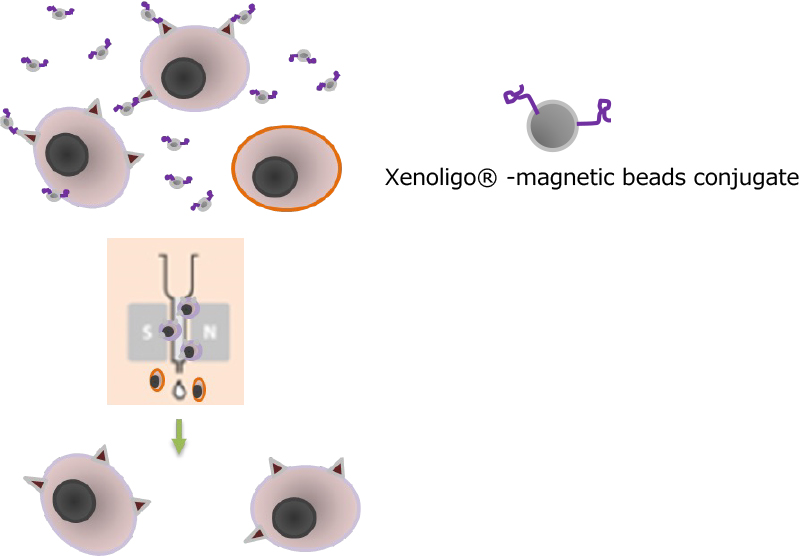
Figure 1: Concept of cell separation with Xenoligo®.
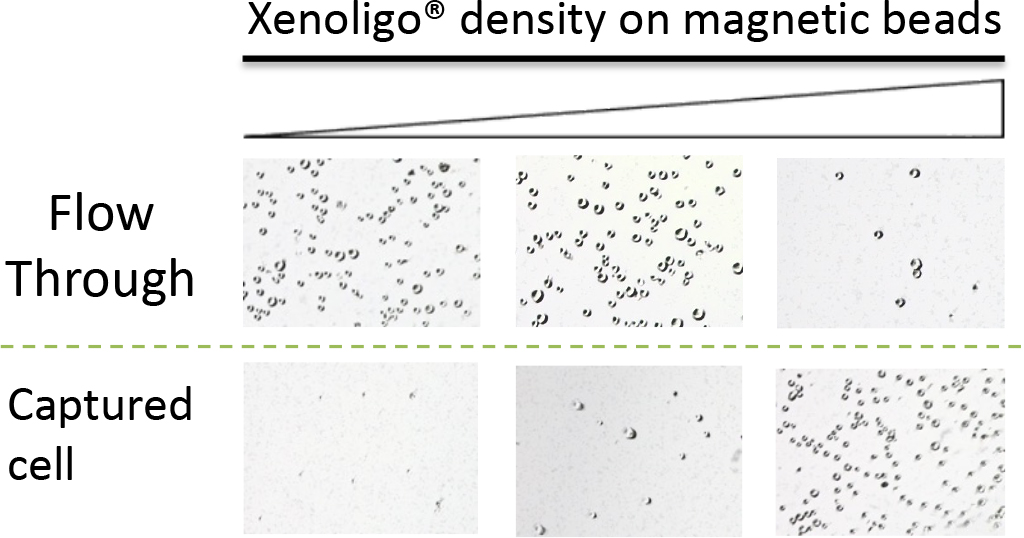
Figure 2. Xenoligo® density-dependent cell separation
