Artificial base pair/Ds-Px
The artificial base pair Ds-Px, developed over many years by founder Dr. Ichiro Hirao, is a base pair that enables amplification of DNA by PCR using DNA polymerase and transcription into RNA by RNA polymerase.
A-T and G-C base pairs form base pairs by hydrogen bonding. On the other hand, Ds-Px base pairs can form base pairs by interlocking the shape of each base. In order to prevent Ds and Px from forming base pairs with other bases, we have devised a number of measures, such as 1) eliminating functional groups that form hydrogen bonds, and 2) incorporating functional groups that cause steric hindrance.
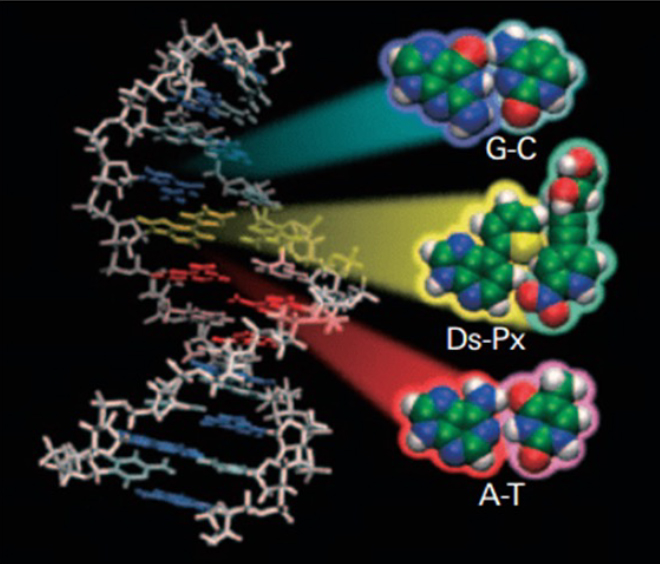
Ref. RIKEN NEWS Aug. 2013
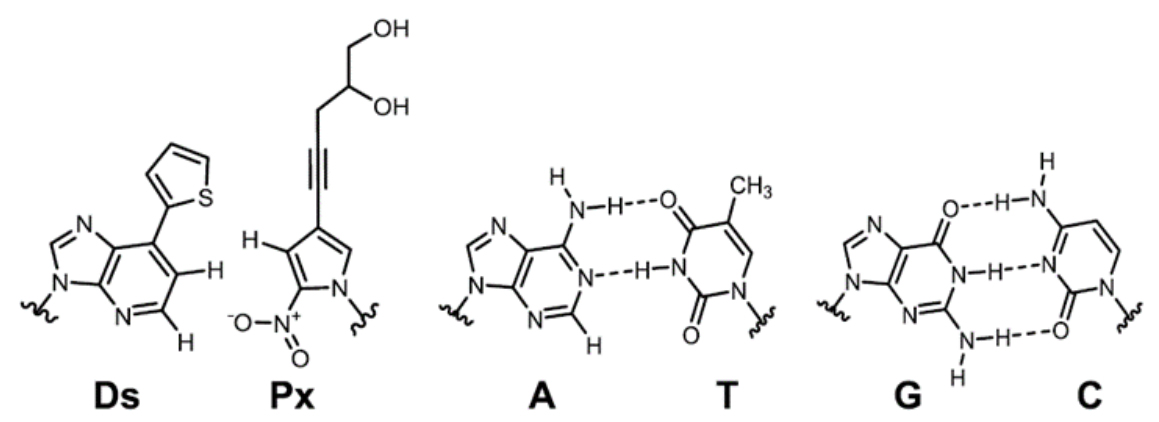
Ref. Futami K. et al. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids (2019) p158-170
SELEX using the artificial base pair Ds-Px
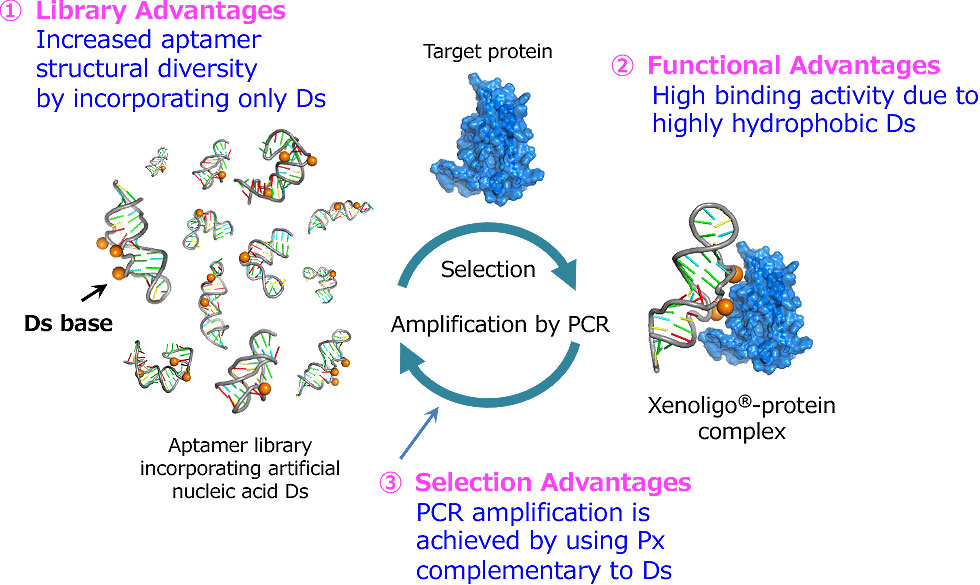
Advantages of using artificial base pairing for selection
① Advantages of Library
The DNA library incorporates the artificial base Ds. The absence of the artificial base Px, which forms base pairs, makes it impossible for Ds to form base pairs and to be involved in stem structures. Therefore, Ds is present in the single-stranded region, such as the bulge-out structure and internal loop structure, and can form a variety of structures.
② Functional advantage
The addition of highly hydrophobic Ds adds a new interaction to the binding with the target molecule. The hydrophobic base moiety is larger than that of purine bases A and T, and is further away from the ribose moiety. This shape allows Ds to interact with pockets of hydrophobic amino acids, which are difficult for natural bases to reach.
Binding studies using oligos with Ds replaced with adenosine (A) have confirmed that the binding affinity for the target protein is reduced, suggesting that the hydrophobic nature of Ds allows it to bind to the target protein.
➂ Selection advantage
The binding sequence recovered by screening must be amplified by PCR. By adding phosphorylated nucleoside of Px, the complementary base of Ds, in the reaction solution, it is possible to amplify the oligonucleotide in which Ds is inserted.
